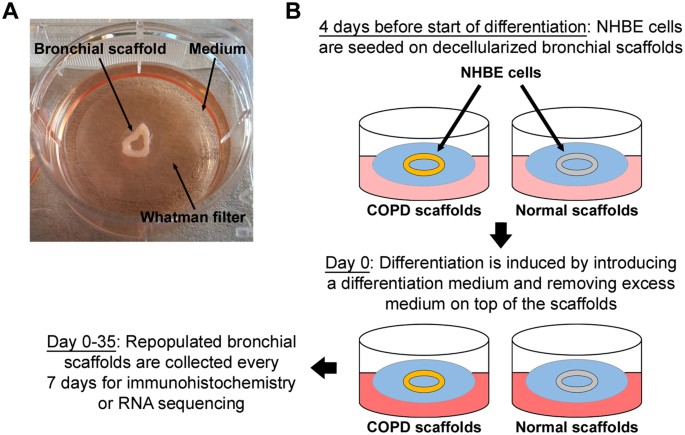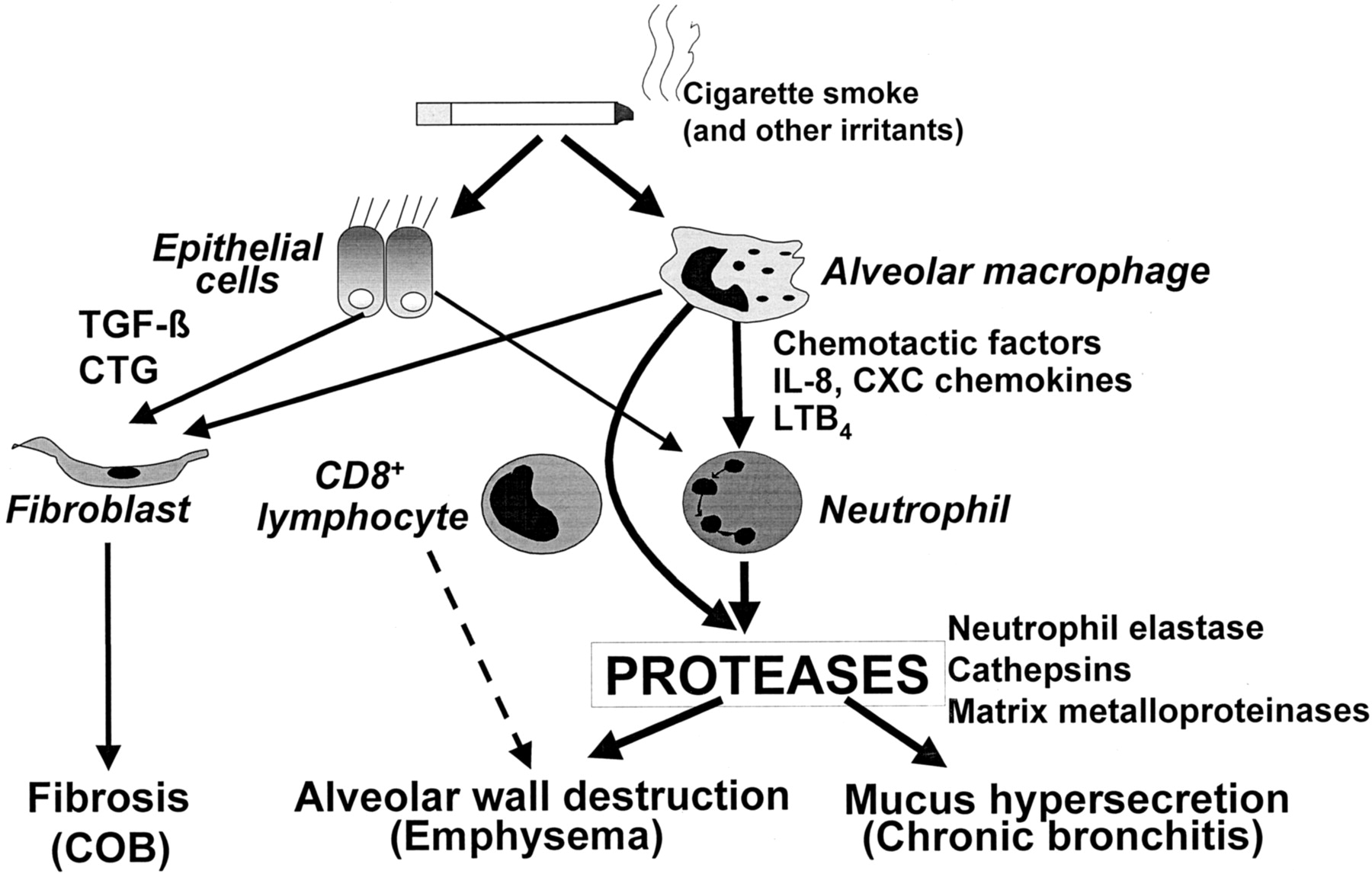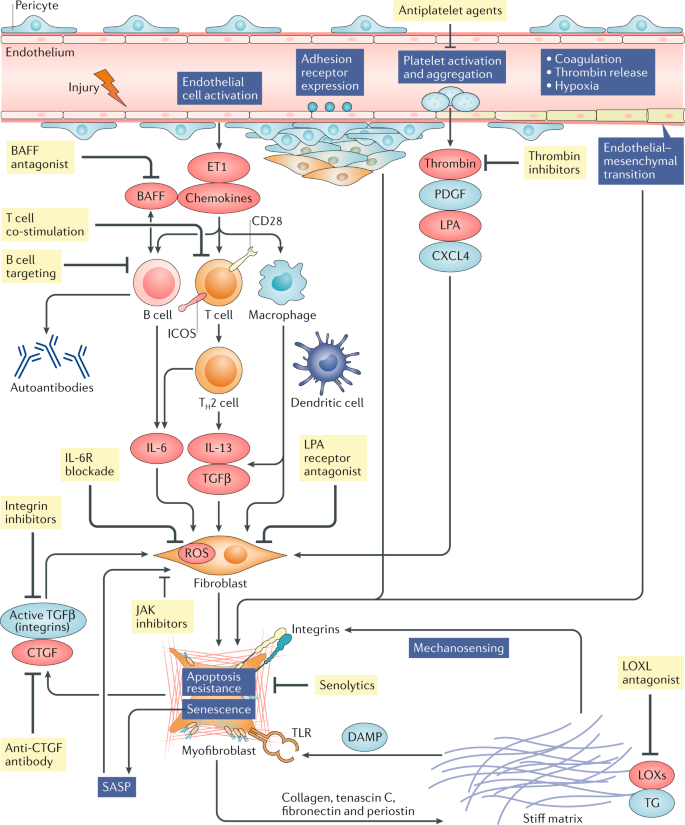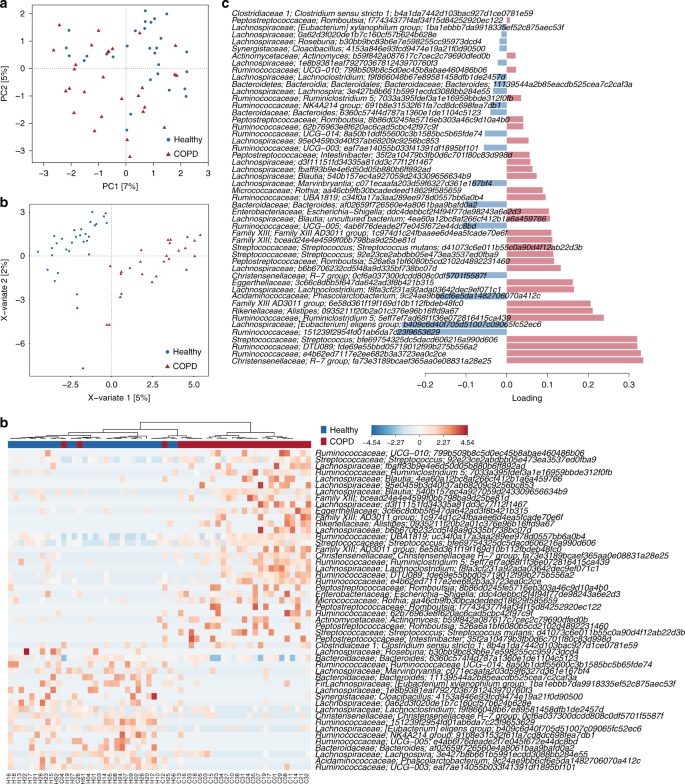
Disease-associated gut microbiome and metabolome changes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Nature Communications
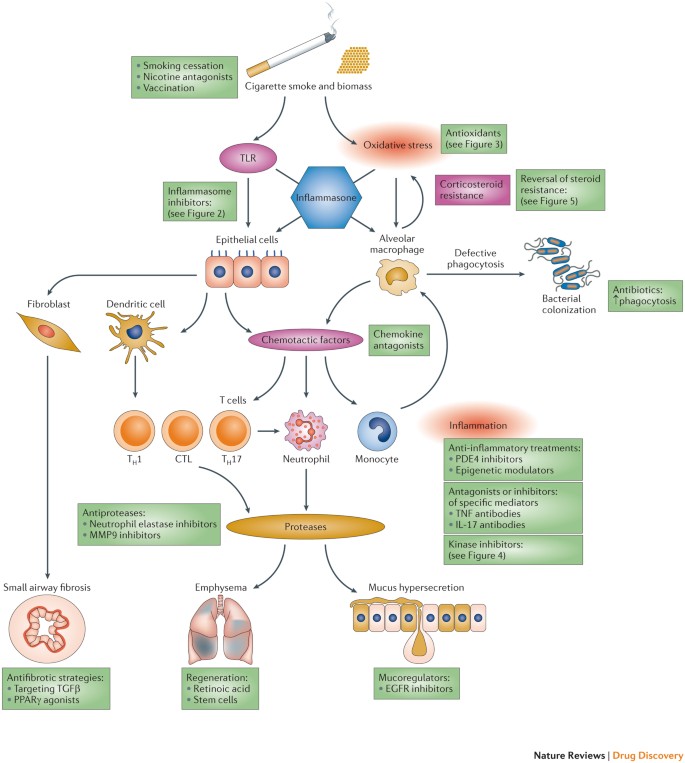
New anti-inflammatory targets for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Nature Reviews Drug Discovery

Respiratory viral infection: a potential “missing link” in the pathogenesis of COPD | European Respiratory Society
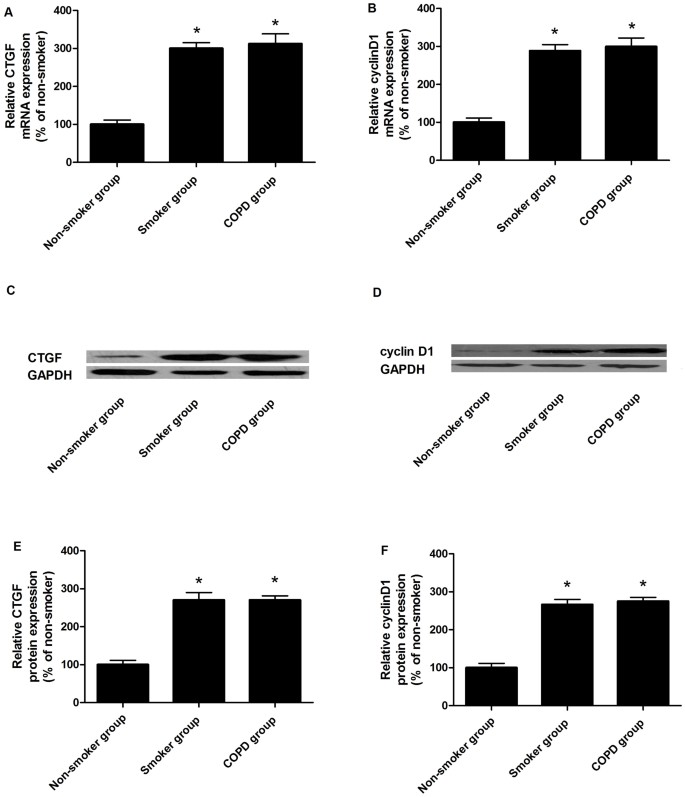
Expression variations of connective tissue growth factor in pulmonary arteries from smokers with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Scientific Reports

CTGF disrupts alveolarization and induces pulmonary hypertension in neonatal mice: implication in the pathogenesis of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): epidemiology, risk factors for developing the disease, mechanisms, and differentia

The Role of Mitochondria and Oxidative/Antioxidative Imbalance in Pathobiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Respiratory viral infection: a potential “missing link” in the pathogenesis of COPD | European Respiratory Society

PDF) Animal Models Reflecting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Related Respiratory Disorders: Translating Pre-Clinical Data into Clinical Relevance
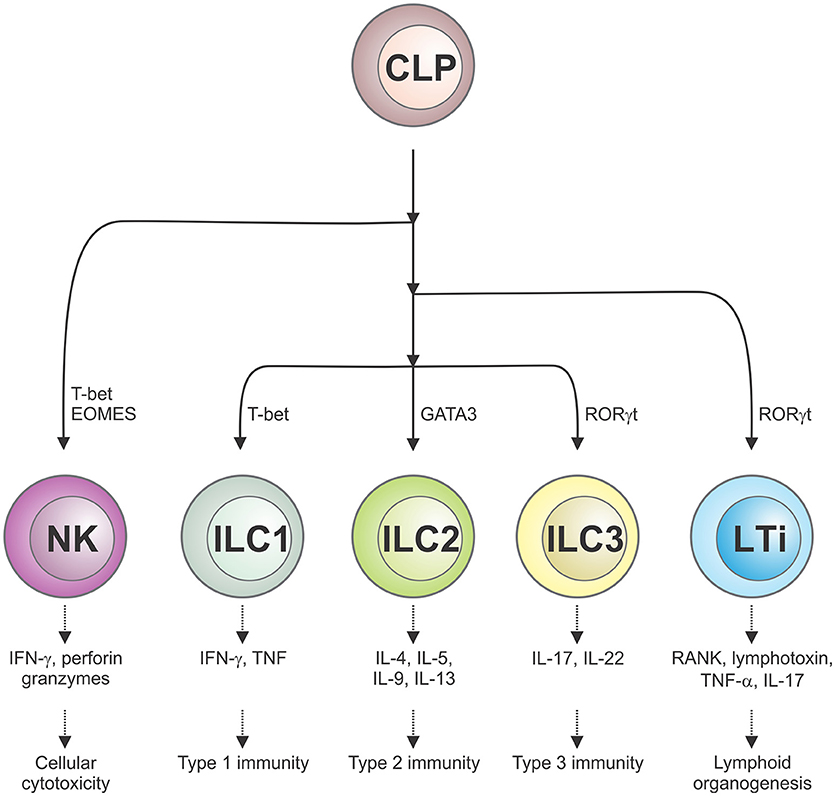
Frontiers | The Influence of Innate Lymphoid Cells and Unconventional T Cells in Chronic Inflammatory Lung Disease | Immunology

The role of macrophages in obstructive airways disease: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma - ScienceDirect
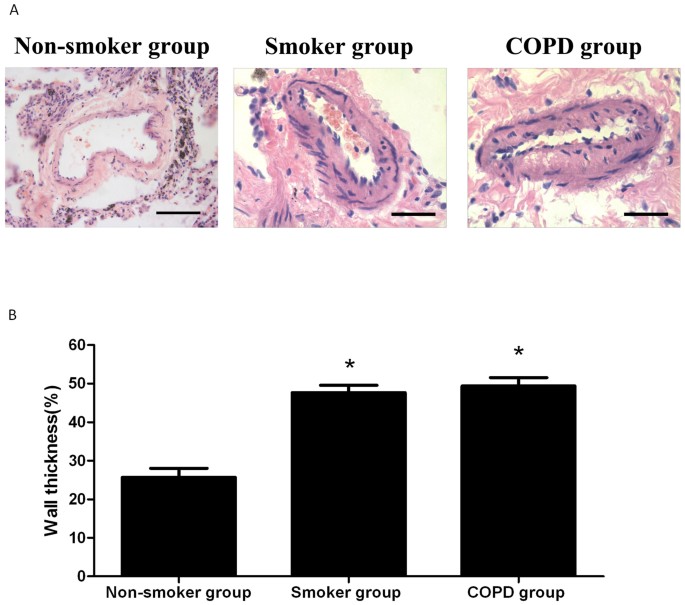
Expression variations of connective tissue growth factor in pulmonary arteries from smokers with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Scientific Reports
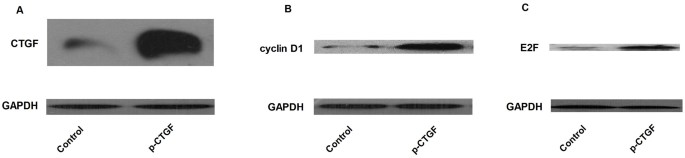
Expression variations of connective tissue growth factor in pulmonary arteries from smokers with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Scientific Reports

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: molecular and cellularmechanisms | European Respiratory Society

Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: molecular and cellularmechanisms | European Respiratory Society